

ATOMIC MASS OF ALUMINUM FREE
However, this assumes the atom to exhibit a spherical shape, which is only obeyed for atoms in vacuum or free space. Aluminum cation Al+27 - structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety. The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the distance out to which the electron cloud extends from the nucleus. It must be noted, atoms lack a well-defined outer boundary. The atomic radius of Aluminium atom is 121pm (covalent radius). Note that, each element may contain more isotopes, therefore this resulting atomic mass is calculated from naturally-occuring isotopes and their abundance. The atomic mass is carried by the atomic nucleus, which occupies only about 10 -12 of the total volume of the atom or less, but it contains all the positive charge and at least 99.95% of the total mass of the atom. The atomic mass or relative isotopic mass refers to the mass of a single particle, and therefore is tied to a certain specific isotope of an element.
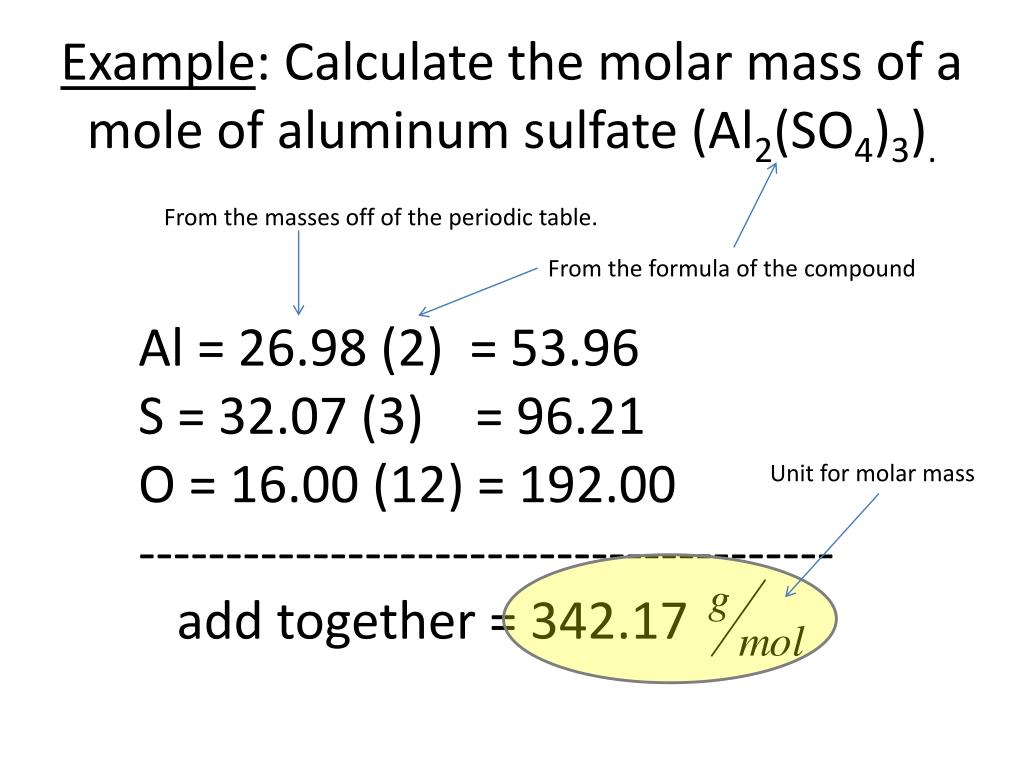
Calculate the number of atoms of aluminum in 15.0 cm3 corundum. Mass numbers of typical isotopes of Aluminium are 27. Compute the mass (in grams) of a single iodine atom if the relative atomic mass of. Isotopes are nuclides that have the same atomic number and are therefore the same element, but differ in the number of neutrons. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.įor stable elements, there is usually a variety of stable isotopes. Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N+Z=A. The total number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom is called the neutron number of the atom and is given the symbol N. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10 -19 coulombs. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. This fact has key implications for the building up of the periodic table of elements.Atomic Number – Protons, Electrons and Neutrons in AluminiumĪluminium is a chemical element with atomic number 13 which means there are 13 protons in its nucleus. The ordering of the electrons in the ground state of multielectron atoms, starts with the lowest energy state (ground state) and moves progressively from there up the energy scale until each of the atom’s electrons has been assigned a unique set of quantum numbers. It is the Pauli exclusion principle that requires the electrons in an atom to occupy different energy levels instead of them all condensing in the ground state. each contain exactly one mole of carbon, sulfur, and aluminum, respectively. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z. 66 X 10-24 grams Molar Mass of a single molecule Grams per mole Molar Mass. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. Therefore, an aluminum atom has fourteen neutrons. The chemical properties of the atom are determined by the number of protons, in fact, by number and arrangement of electrons. We know that the atomic number of aluminum is 13 and the atomic mass number is about 27. See also: Atomic Number – Does it conserve in a nuclear reaction? Atomic Number and Chemical PropertiesĮvery solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms.

It is the electrons that are responsible for the chemical bavavior of atoms, and which identify the various chemical elements. In a neutral atom there are as many electrons as protons moving about nucleus. The nucleus is composed of protons and neutrons. The atom consist of a small but massive nucleus surrounded by a cloud of rapidly moving electrons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
